Standard nerve surgery for leg amputation should prevent postamputation pain
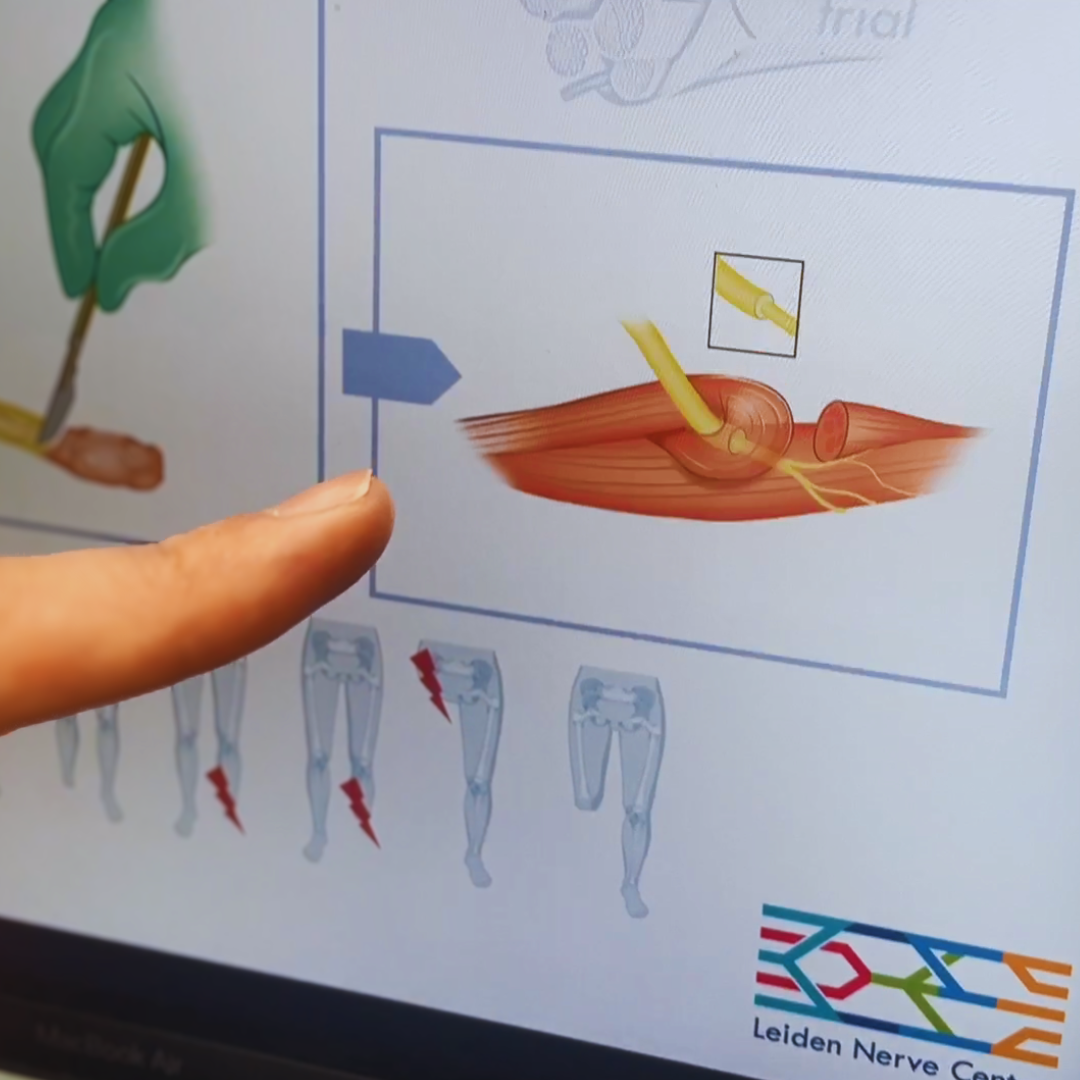
During the surgery, the surgeons attach the severed nerve to the nerve ending of the muscle in the stump.
&width=710&height=710)
In the Netherlands, around 3,300 leg amputations are performed annually. Currently, the standard procedure is for a surgeon to tie off or burn the ends of the severed nerves, which leaves nerve damage in the stump. In more than half of the cases, this leads to post-amputation pain such as phantom pain, the pain felt in an amputated limb. This pain can severely impact a person’s daily functioning and lead to high medication use.
Giving the nerve something to do
Each nerve has a regenerative ability, the ability to heal itself. A severed nerve will therefore grow out, seeking to connect with the rest of the nervous system. This nerve scar can cause a lot of pain. "Neatly cutting and storing it can help, but even better is to give the nerve something to do," says neurosurgeon Justus Groen. "In this case, we do this by attaching the severed nerve to the nerve ending of a muscle in the stump. Because the nerve has a connection again, it will not form a painful nerve scar. That is the biggest gain. The result is that people can start mobilizing after the amputation and, for example, wear a prosthesis."
Procedure to prevent phantom pain
The technique described by Groen is not new. In practice, it has already been shown that the method works. However, this procedure is usually performed only after a patient has developed post-amputation pain, often weeks or months after the amputation itself. The downside is that the patient has to undergo surgery again.
The LUMC and six other Dutch hospitals want to perform the nerve surgery preventively, at the time when the leg is being amputated and the patient is still on the operating table. To provide definitive scientific proof that the method works, the involved centers, led by the LUMC, will start a study this summer. Doctors estimate that the nerve surgery will only add half an hour to the operation time.
Collaboration between Neurosurgeons, Vascular Surgeons, and Rehabilitation Physicians
For the research, neurosurgeons, vascular surgeons, and rehabilitation physicians at the LUMC will work closely together. The vascular surgeon performs the amputation, and the neurosurgeon connects the nerve. Later, the intention is for vascular surgeons to also perform the nerve procedure. Vascular surgeon Jan van Schaik: "I know the technique, but it’s like setting up a tent: practice can be slightly different. You need to have done it a few times to get it just right. That's why we'll do it together the first few times."
Rehabilitation physicians are also involved in the research. They see the patients after the amputation and look at, among other things, functional improvement and prosthesis use.
Future
The study will include 260 patients with peripheral vascular disease (also known as intermittent claudication) who need to undergo leg amputation. The nerve operation may also benefit people who lose a leg for other reasons in the future. The first results of the new study are expected in five years.
The patient association "Korter Maar Krachtig" emphasizes the importance of this study.
Video: Onderzoek om fantoompijn te voorkomen
&width=826&height=464)
&width=400&height=400)